El lijado de superficies planas barnizadas es una operación habitual en la industria de la madera, los tableros y la...
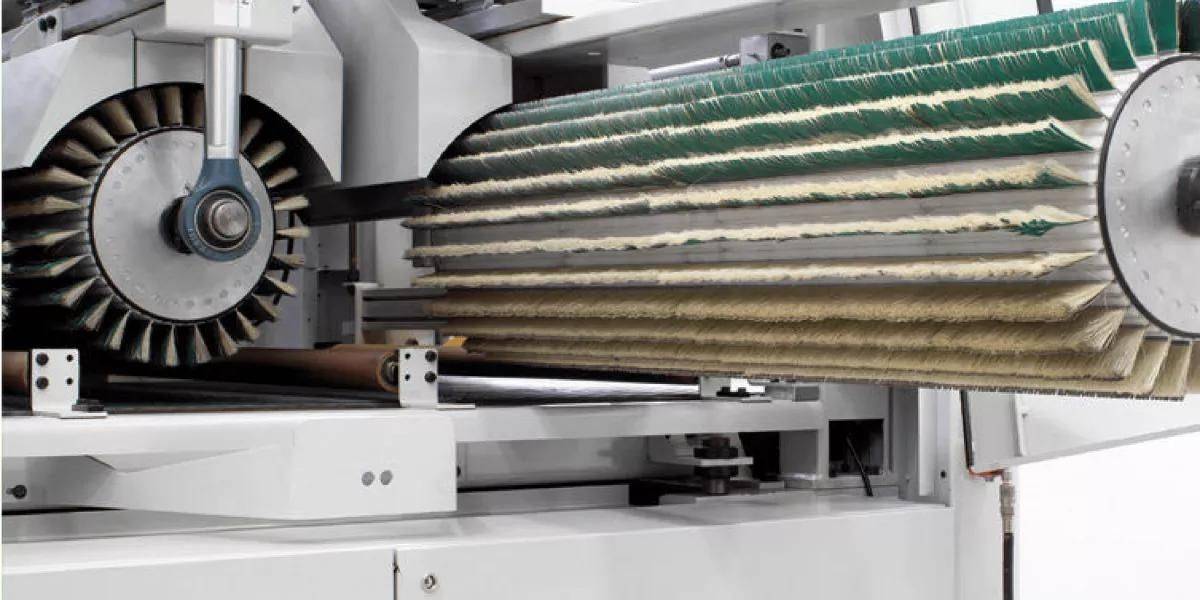
}Sanding brushes, with interchangeable abrasive strips, are increasingly used for sanding all types of raw wood surfaces, varnished wood, metal or composite materials.
They are the ideal solution for sanding edges, burrs, intermediate sanding of profiles and soft sanding of deep profiles where flexibility and adaptation to surfaces is required.
Sanding brushes are very effective tools compared to manual sanding work and can in some cases replace portable orbital sanders.
As each sanding application is different, a certain brush setting is required to suit the surface or trim to be treated.
In every sanding brush system we find two basic elements:
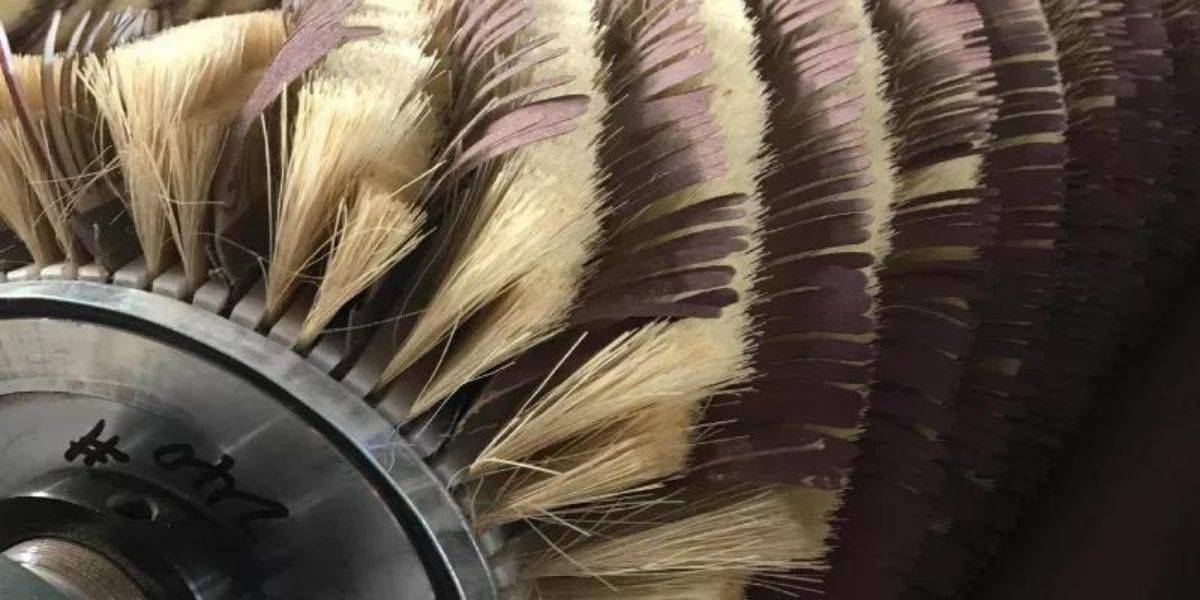
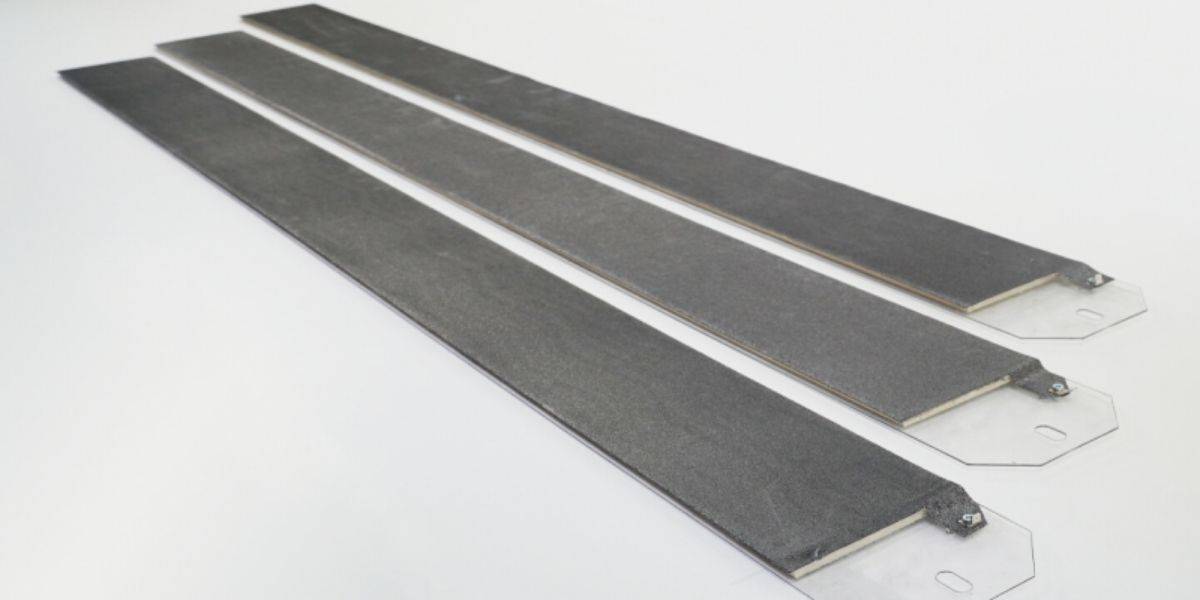
Interchangeable sanding strips, also called abrasive strips.
And the sanding heads, cores or rotors.
Interchangeable sanding strips
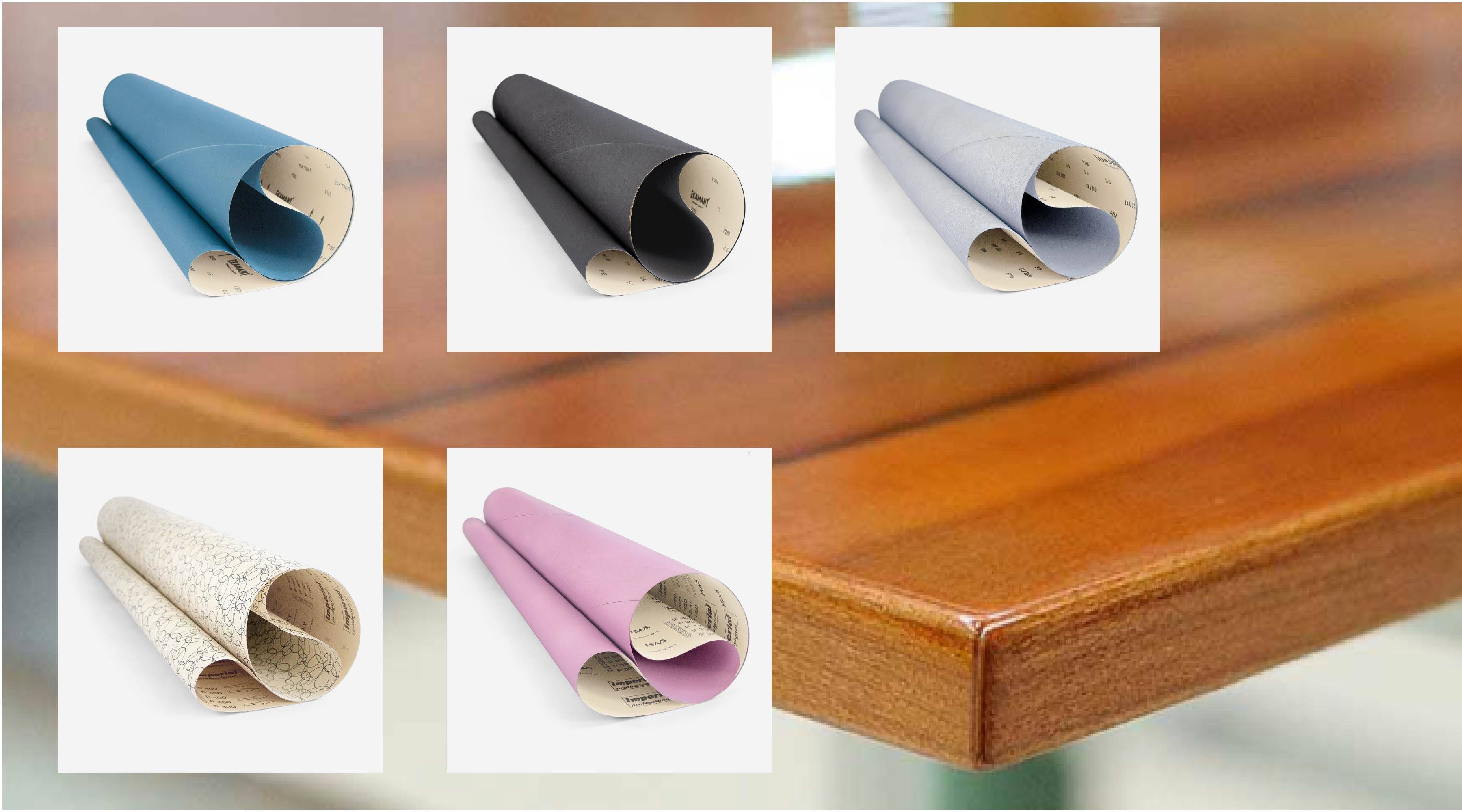
The strips, or abrasive strips, are made up of the abrasive sheet, the support fibers and the plastic guide on which they are held.
The sanding sheet is an abrasive cloth. Your choice is key, and it depends on the type of material we want to sand (wood, metal or composites), the degree of flexibility that the sanding operation requires and the desired level of finish.
The support fibers are usually vegetable fibers, although sometimes horse hair fibers or synthetic fibers are also used. The function of these fibers is to serve as a backing for the abrasive strip, keeping it upright during sanding, providing flexibility and consistency during work.
The plastic or metal guide allows the holding of the abrasive and the hair fibers. These guides are subsequently inserted into the grooves of the sanding heads that the different machines have incorporated. Each manufacturer assembles their own heads with their own design of the shape of the slot.
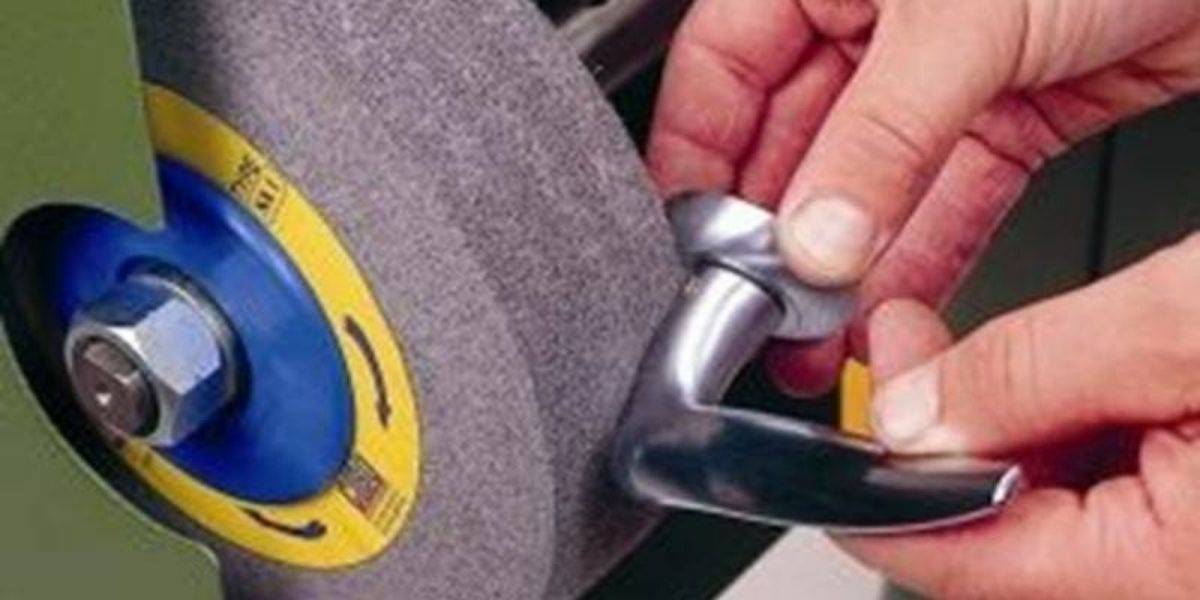
Sanding heads
Typically, sanding heads, cores or rotors are made up of a system of equal modules that are coupled together. In this way, we have great flexibility since it allows us to mount heads in all possible sizes, adapting to each of the existing machines on the market.
In general, the heads or rotors are made of a highly rigid thermoplastic material, which provides rigidity and dimensional stability to the assembly once the abrasive strips or strips are assembled.
Depending on the manufacturer, the cores are available in various diameters and number of grooves. The most common diameters and densities are:
Ø 50 mm with 10 slots
Ø 80 mm with 20 slots
Ø 100 mm with 20 slots
Ø 120 mm with 24 slots
Ø 180 mm with 36 slots
Ø 280 mm with 20 slots
The sanding strips inserted in the head grooves are held in place by a cap or a ring system that holds them in place, and facilitates a quick change of the strips.
The sanding systems with interchangeable strips are very versatile, and can also be used in heads of numerical control machines and / or profiling machines for sanding the edges.
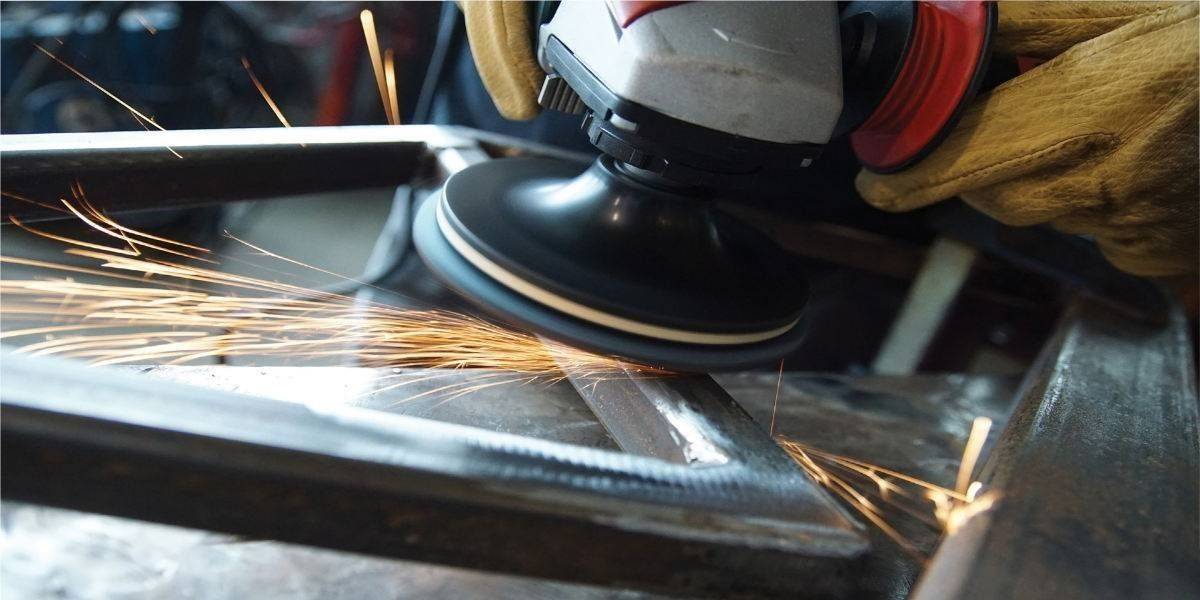
The automation needs of certain manual jobs have led to the use of disk-shaped heads for sanding edges and profiles on all wood surfaces. In this system, the sanding strips are arranged radially on the sanding plate, acting at a sanding angle with respect to the surface, which facilitates the evacuation of dust and a higher performance of the abrasive head. By means of this system it is possible to sand both profiled moldings and flat surfaces.
Four variables to take into account
The shape of the anchor of the plastic guide.
Although each abrasive manufacturer uses its own design, the systems are generally compatible with each other. Having a physical sample to insert into the slot and check its operation is in the end the safest way to get it right (the strip should not come out, but neither should it enter too tight or have a lot of slack)
The length of the protrusion of the sandpaper.
Larger or longer sanding protrusions are used to reach deeper surfaces; on the contrary, the smaller or shorter projections are used for sanding flat surfaces or those with little pronounced curves.
The most common sanding projections, among the different manufacturers, are 30, 40, 45, 55 and 70 mm. Although projections can be made to measure.
The measurement of the width of the fringe or cut of the sandpaper.
Depending on the shape and depth of the profile to be sanded, different widths can be used when cutting the sandpaper. Narrower cuts create fringes that fit and penetrate better in the tightest spaces, while wider cuts are ideal for flat or smoothly curved surfaces with easy access.
The most common cutting widths are 3, 4, 5, 7, 14 and 20 mm.
It is common practice to alternate strips with two different fringe widths on the same rotor. In this way, more versatile sanding brushes are available for the different shapes to be sanded.
The type of abrasive mineral.
Depending on the type of material that we are going to sand, it will be convenient to use one mineral or another. In general, aluminum oxide mineral is used for sanding raw wood and for intermediate sanding of varnish. Silicon carbide mineral is suitable for sanding fibreboard and for fine sanding of varnished surfaces, especially water-based. While ceramic minerals are used for metal work.
Sanding strips are generally made of abrasive cloth. Although there is a huge multitude of abrasive fabrics on the market; It is very important to have a balance between the flexibility of your support, its resistance and the ability of the fabric to fray as the abrasive mineral wears away.
Sanding brushes with interchangeable abrasive blades have long been very effective sanding tools in the wood and varnish industry. They save time and costs in sanding operations, while providing a uniform and regular finish.
They are used especially for the manufacture of interior doors, exterior doors and kitchen furniture doors; Business sectors in which Abracom has been operating for more than 35 years, distributing efficient sanding systems for the wood and its derivatives industry. We are manufacturers of abrasive belts, discs and sheets. For any question or clarification, contact us.






















 (1).png)
 (1).png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)







